File size: 6,722 Bytes
0588cb6 c6e9cd8 0588cb6 c6e9cd8 0588cb6 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 |
---
license: other
license_name: glm-4
license_link: https://huggingface.co/THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat-hf/blob/main/LICENSE
language:
- en
- zh
base_model:
- THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat-1m
new_version: THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat-1m-hf
pipeline_tag: text-generation
library_name: transformers
tags:
- chatglm
inference: false
---
# GLM-4-9B-Chat-1M
中文阅读,请看[这里](README_zh.md).
If you are using the weights from this repository, please update to
<span style="color:red; font-weight:bold;"> transformers>=4.46.0 </span>
These weights are **not compatible** with older versions of the transformers library.
## Model Introduction
GLM-4-9B is the open-source version of the latest generation of pre-trained models in the GLM-4 series launched by Zhipu
AI. In the evaluation of data sets in semantics, mathematics, reasoning, code, and knowledge, **GLM-4-9B**
and its human preference-aligned version **GLM-4-9B-Chat** have shown superior performance beyond Llama-3-8B. In
addition to multi-round conversations, GLM-4-9B-Chat also has advanced features such as web browsing, code execution,
custom tool calls (Function Call), and long text
reasoning (supporting up to 128K context). This generation of models has added multi-language support, supporting 26
languages including Japanese, Korean, and German. We have also launched the **GLM-4-9B-Chat-1M** model that supports 1M
context length (about 2 million Chinese characters) and the multimodal model GLM-4V-9B based on GLM-4-9B.
**GLM-4V-9B** possesses dialogue capabilities in both Chinese and English at a high resolution of 1120*1120.
In various multimodal evaluations, including comprehensive abilities in Chinese and English, perception & reasoning,
text recognition, and chart understanding, GLM-4V-9B demonstrates superior performance compared to
GPT-4-turbo-2024-04-09, Gemini 1.0 Pro, Qwen-VL-Max, and Claude 3 Opus.
### Long Context
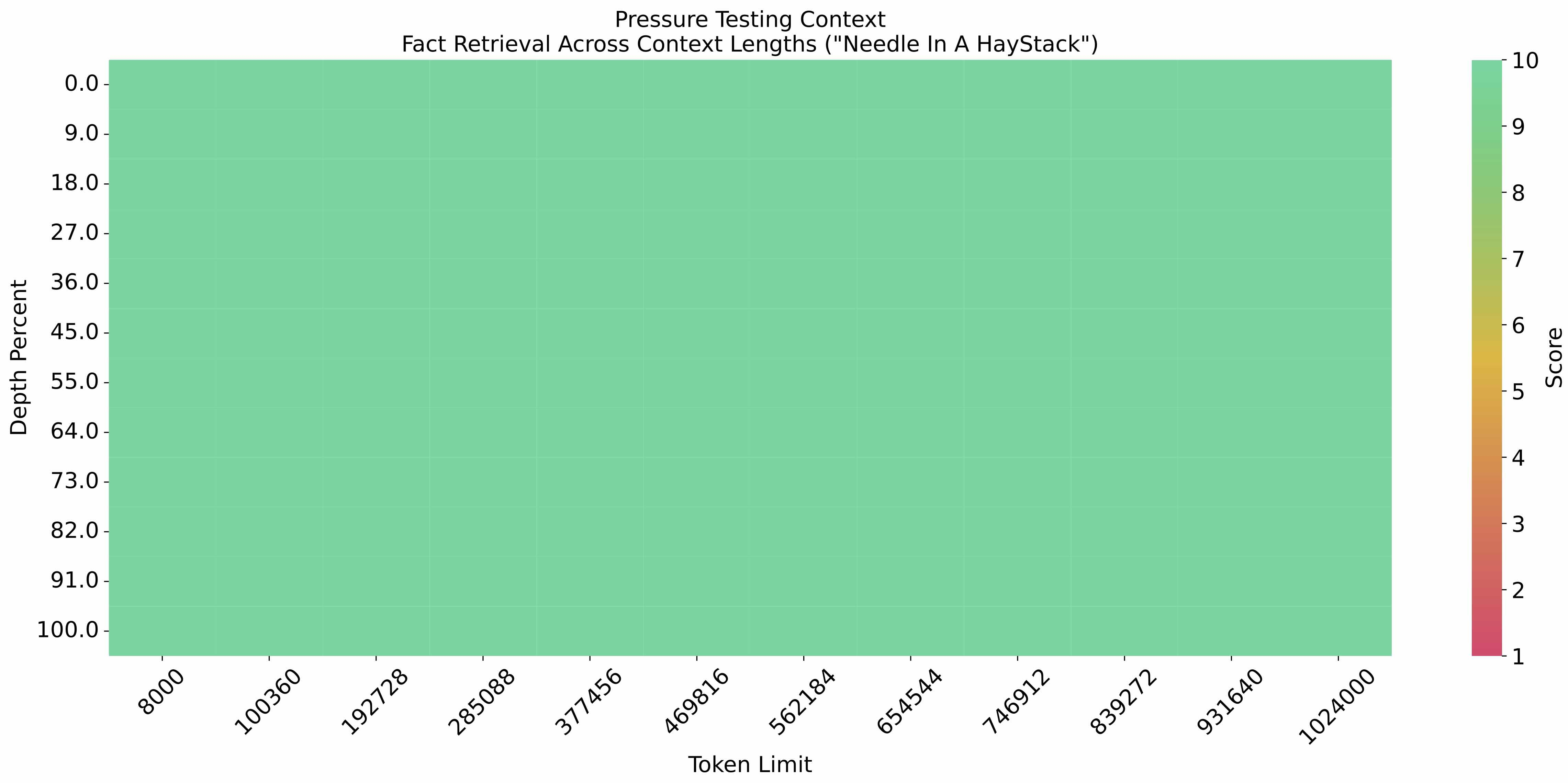
The [eval_needle experiment](https://github.com/LargeWorldModel/LWM/blob/main/scripts/eval_needle.py) was conducted with
a context length of 1M, and the results are as follows:
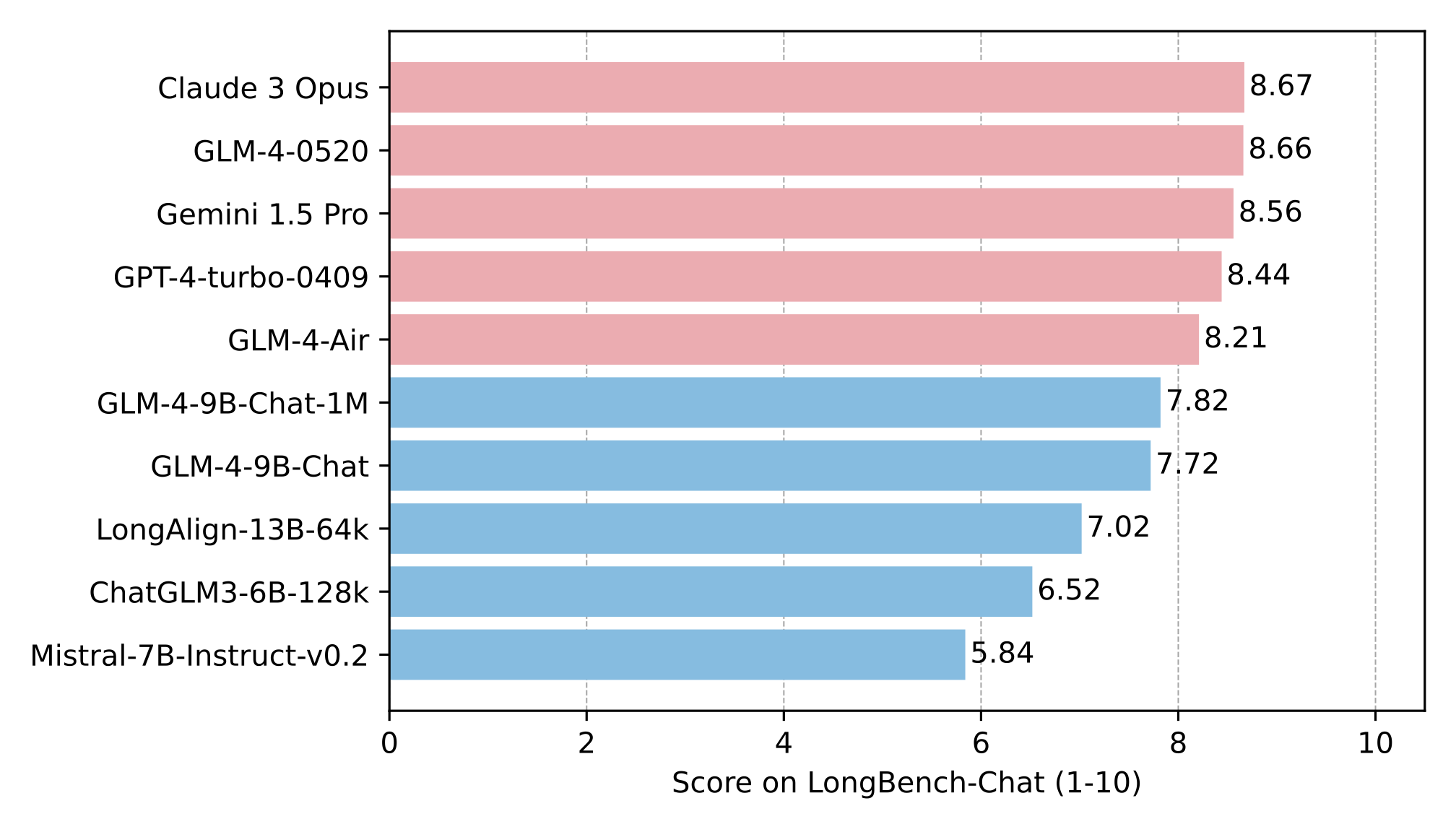
The long text capability was further evaluated on LongBench, and the results are as follows:
**This repository is the model repository of GLM-4-9B-Chat-1M, supporting `1M` context length.**
## Quick Start
**For more inference code and requirements, please visit our [github page](https://github.com/THUDM/GLM-4).**
**Please strictly follow the [dependencies](https://github.com/THUDM/GLM-4/blob/main/basic_demo/requirements.txt) to
install, otherwise it will not run properly**
### Use the following method to quickly call the GLM-4-9B-Chat-1M language model
Use the transformers backend for inference:
```python
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
MODEL_PATH = 'THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat-1m-hf'
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(MODEL_PATH)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(MODEL_PATH, device_map="auto")
message = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "Answer the following question."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "How many legs does a cat have?"
}
]
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
message,
return_tensors='pt',
add_generation_prompt=True,
return_dict=True,
).to(model.device)
input_len = inputs['input_ids'].shape[1]
generate_kwargs = {
"input_ids": inputs['input_ids'],
"attention_mask": inputs['attention_mask'],
"max_new_tokens": 128,
"do_sample": False,
}
out = model.generate(**generate_kwargs)
print(tokenizer.decode(out[0][input_len:], skip_special_tokens=True))
```
### vLLM Lib(0.6.4 and later version) for inference:
```Python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
# THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat-1m-hf
# max_model_len, tp_size = 1048576, 4
# If you encounter OOM phenomenon, it is recommended to reduce max_model_len or increase tp_size
max_model_len, tp_size = 131072, 1
model_name = "THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat-1m-hf"
prompt = [{"role": "user", "content": "what is your name?"}]
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name, trust_remote_code=True)
llm = LLM(
model=model_name,
tensor_parallel_size=tp_size,
max_model_len=max_model_len,
trust_remote_code=True,
enforce_eager=True,
# GLM-4-9B-Chat-1M-HF If you encounter OOM phenomenon, it is recommended to enable the following parameters
# enable_chunked_prefill=True,
# max_num_batched_tokens=8192
)
stop_token_ids = [151329, 151336, 151338]
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.95, max_tokens=1024, stop_token_ids=stop_token_ids)
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(prompt, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
outputs = llm.generate(prompts=inputs, sampling_params=sampling_params)
print(outputs[0].outputs[0].text)
```
## LICENSE
The weights of the GLM-4 model are available under the terms of [LICENSE](LICENSE)
## Citations
If you find our work useful, please consider citing the following paper.
```
@misc{glm2024chatglm,
title={ChatGLM: A Family of Large Language Models from GLM-130B to GLM-4 All Tools},
author={Team GLM and Aohan Zeng and Bin Xu and Bowen Wang and Chenhui Zhang and Da Yin and Diego Rojas and Guanyu Feng and Hanlin Zhao and Hanyu Lai and Hao Yu and Hongning Wang and Jiadai Sun and Jiajie Zhang and Jiale Cheng and Jiayi Gui and Jie Tang and Jing Zhang and Juanzi Li and Lei Zhao and Lindong Wu and Lucen Zhong and Mingdao Liu and Minlie Huang and Peng Zhang and Qinkai Zheng and Rui Lu and Shuaiqi Duan and Shudan Zhang and Shulin Cao and Shuxun Yang and Weng Lam Tam and Wenyi Zhao and Xiao Liu and Xiao Xia and Xiaohan Zhang and Xiaotao Gu and Xin Lv and Xinghan Liu and Xinyi Liu and Xinyue Yang and Xixuan Song and Xunkai Zhang and Yifan An and Yifan Xu and Yilin Niu and Yuantao Yang and Yueyan Li and Yushi Bai and Yuxiao Dong and Zehan Qi and Zhaoyu Wang and Zhen Yang and Zhengxiao Du and Zhenyu Hou and Zihan Wang},
year={2024},
eprint={2406.12793},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={id='cs.CL' full_name='Computation and Language' is_active=True alt_name='cmp-lg' in_archive='cs' is_general=False description='Covers natural language processing. Roughly includes material in ACM Subject Class I.2.7. Note that work on artificial languages (programming languages, logics, formal systems) that does not explicitly address natural-language issues broadly construed (natural-language processing, computational linguistics, speech, text retrieval, etc.) is not appropriate for this area.'}
}
``` |