File size: 4,513 Bytes
01e337b 72fdc69 01e337b daf2a0a 72fdc69 daf2a0a 51fc1ff daf2a0a 72fdc69 daf2a0a 72fdc69 daf2a0a 72fdc69 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 |
---
tags:
- pytorch_model_hub_mixin
- model_hub_mixin
- multimodal
license: cc-by-nc-sa-4.0
---
# ImageBind: One Embedding Space To Bind Them All
**[FAIR, Meta AI](https://ai.facebook.com/research/)**
To appear at CVPR 2023 (*Highlighted paper*)
[[`Paper`](https://facebookresearch.github.io/ImageBind/paper)] [[`Blog`](https://ai.facebook.com/blog/imagebind-six-modalities-binding-ai/)] [[`Demo`](https://imagebind.metademolab.com/)] [[`Supplementary Video`](https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/imagebind/imagebind_video.mp4)] [[`BibTex`](#citing-imagebind)]
PyTorch implementation and pretrained models for ImageBind. For details, see the paper: **[ImageBind: One Embedding Space To Bind Them All](https://facebookresearch.github.io/ImageBind/paper)**.
ImageBind learns a joint embedding across six different modalities - images, text, audio, depth, thermal, and IMU data. It enables novel emergent applications ‘out-of-the-box’ including cross-modal retrieval, composing modalities with arithmetic, cross-modal detection and generation.
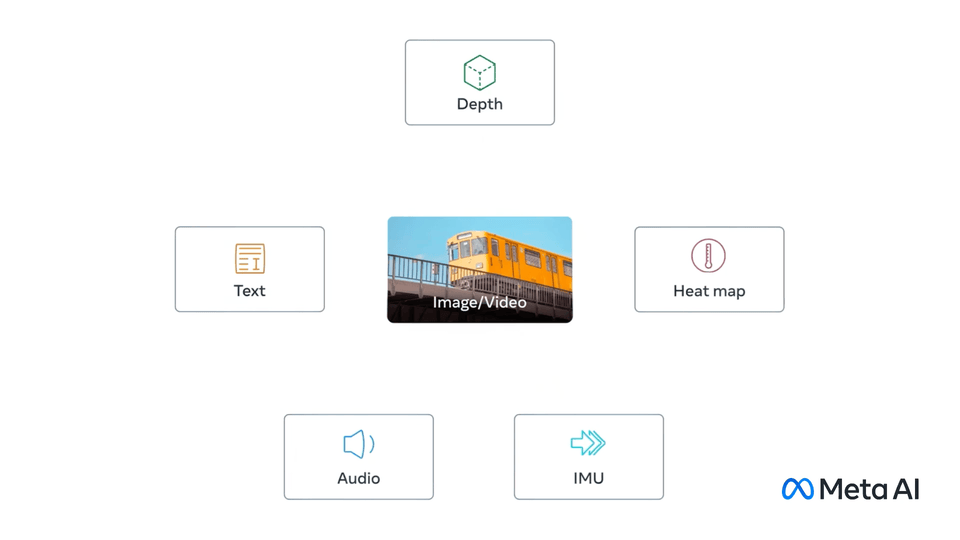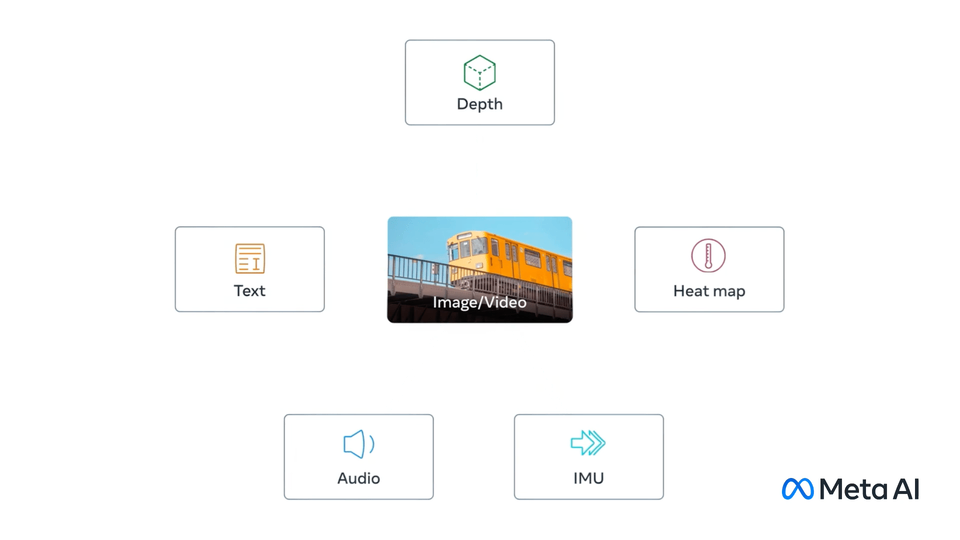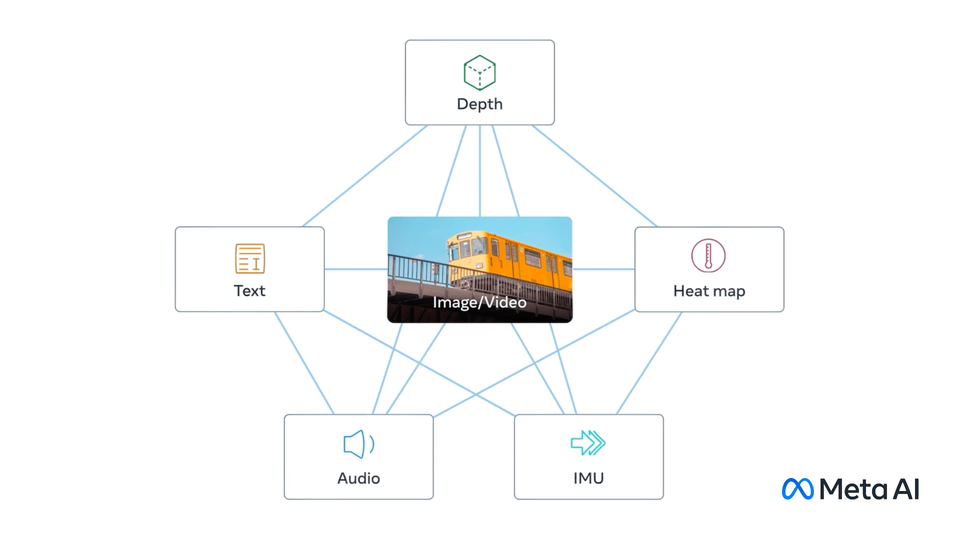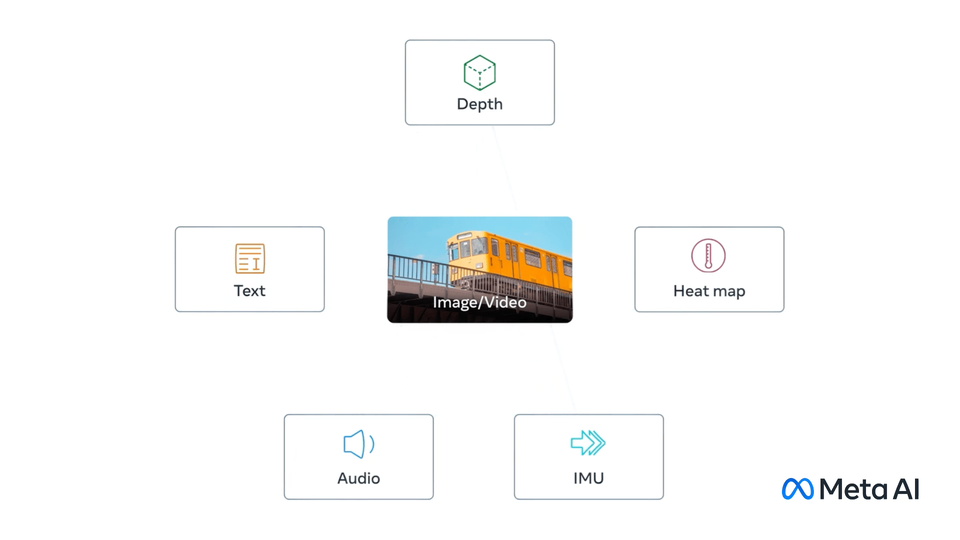
## ImageBind model
Emergent zero-shot classification performance.
<table style="margin: auto">
<tr>
<th>Model</th>
<th><span style="color:blue">IN1k</span></th>
<th><span style="color:purple">K400</span></th>
<th><span style="color:green">NYU-D</span></th>
<th><span style="color:LightBlue">ESC</span></th>
<th><span style="color:orange">LLVIP</span></th>
<th><span style="color:purple">Ego4D</span></th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>imagebind_huge</td>
<td align="right">77.7</td>
<td align="right">50.0</td>
<td align="right">54.0</td>
<td align="right">66.9</td>
<td align="right">63.4</td>
<td align="right">25.0</td>
</tr>
</table>
## Usage
First git clone the repository:
```bash
git clone -b feature/add_hf https://github.com/nielsrogge/ImageBind.git
cd ImageBind
```
Next, install pytorch 1.13+ and other 3rd party dependencies.
```shell
conda create --name imagebind python=3.8 -y
conda activate imagebind
pip install .
```
For windows users, you might need to install `soundfile` for reading/writing audio files. (Thanks @congyue1977)
```
pip install soundfile
```
Extract and compare features across modalities (e.g. Image, Text and Audio).
```python
from imagebind import data
import torch
from imagebind.models import imagebind_model
from imagebind.models.imagebind_model import ModalityType
from imagebind.models.imagebind_model import ImageBindModel
text_list=["A dog.", "A car", "A bird"]
image_paths=[".assets/dog_image.jpg", ".assets/car_image.jpg", ".assets/bird_image.jpg"]
audio_paths=[".assets/dog_audio.wav", ".assets/car_audio.wav", ".assets/bird_audio.wav"]
device = "cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
model = ImageBindModel.from_pretrained("nielsr/imagebind-huge")
model.eval()
model.to(device)
# Load data
inputs = {
ModalityType.TEXT: data.load_and_transform_text(text_list, device),
ModalityType.VISION: data.load_and_transform_vision_data(image_paths, device),
ModalityType.AUDIO: data.load_and_transform_audio_data(audio_paths, device),
}
with torch.no_grad():
embeddings = model(inputs)
print(
"Vision x Text: ",
torch.softmax(embeddings[ModalityType.VISION] @ embeddings[ModalityType.TEXT].T, dim=-1),
)
print(
"Audio x Text: ",
torch.softmax(embeddings[ModalityType.AUDIO] @ embeddings[ModalityType.TEXT].T, dim=-1),
)
print(
"Vision x Audio: ",
torch.softmax(embeddings[ModalityType.VISION] @ embeddings[ModalityType.AUDIO].T, dim=-1),
)
# Expected output:
#
# Vision x Text:
# tensor([[9.9761e-01, 2.3694e-03, 1.8612e-05],
# [3.3836e-05, 9.9994e-01, 2.4118e-05],
# [4.7997e-05, 1.3496e-02, 9.8646e-01]])
#
# Audio x Text:
# tensor([[1., 0., 0.],
# [0., 1., 0.],
# [0., 0., 1.]])
#
# Vision x Audio:
# tensor([[0.8070, 0.1088, 0.0842],
# [0.1036, 0.7884, 0.1079],
# [0.0018, 0.0022, 0.9960]])
```
## License
ImageBind code and model weights are released under the CC-BY-NC 4.0 license. See [LICENSE](LICENSE) for additional details.
## Citation
```
@inproceedings{girdhar2023imagebind,
title={ImageBind: One Embedding Space To Bind Them All},
author={Girdhar, Rohit and El-Nouby, Alaaeldin and Liu, Zhuang
and Singh, Mannat and Alwala, Kalyan Vasudev and Joulin, Armand and Misra, Ishan},
booktitle={CVPR},
year={2023}
}
``` |